Intel unveiled its new Emerald Rapids processors, part of its 5th-Gen Xeon Scalable lineup. The new processors arrive with multiple features designed to enhance performance across workloads, including AI and HPC.
This is the second Xeon family upgrade in less than a year, providing more compute power and faster memory while maintaining the same power envelope as the previous generation.
Emerald Rapids
Intel has launched its 5th Gen Intel Xeon processors (code-named Emerald Rapids) at its recent “AI Everywhere” event. These processors are designed to deliver increased performance per watt and lower total cost of ownership (TCO) across various critical workloads, including artificial intelligence (AI), high-performance computing (HPC), networking, storage, database, and security.
The new processors support up to 64 cores per CPU, nearly 3x the maximum last-level cache from the previous generation, eight channels of DDR5 per CPU, and offer increased inter-socket bandwidth. They also support CXL Type 3 workflows through leading cloud service providers.
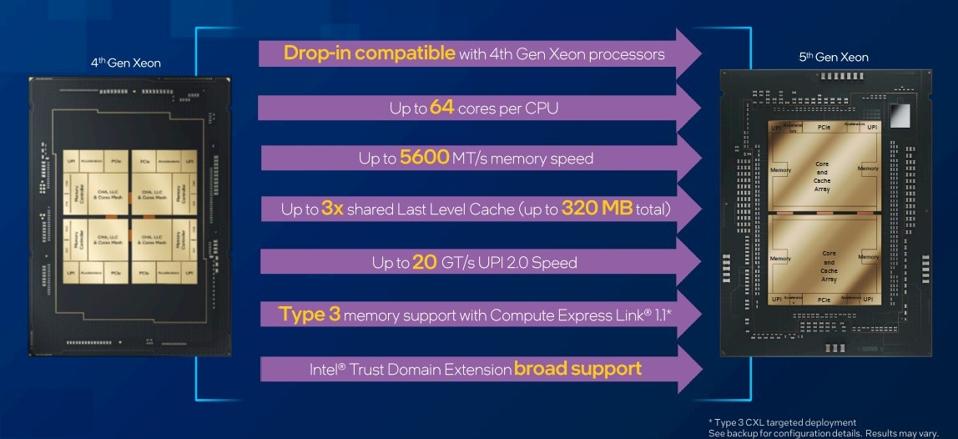
These enhancements work together to deliver an average performance gain of 21% for general compute performance and enable 36% higher average performance per watt across various customer workloads.
Emerald Rapids also supports the full gamut of Intel silicon security features. Intel Trust Domain Extensions (Intel TDX) enhances confidentiality and security at the virtual machine (VM) level, isolating guest operating systems and VM applications from cloud host and hypervisor access.
The 5th Gen Xeon processors are pin-compatible with the previous generation, allowing customers to upgrade infrastructure while reducing costs and carbon emissions.
Embedded Accelerators
Embedded acceleration is a standout feature of Emerald Rapids, with several acceleration technologies designed to boost performance for specific workloads. These include purpose-built accelerators for compression, encryption, and data analytics tasks.
The processors can be configured with various accelerator ‘devices’, providing flexibility based on workload requirements. Types of accelerators such as Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel AMX) and Intel QuickAssist Technology (Intel QAT) underscore Intel’s focus on providing tailored performance boosts for specific applications.
Using accelerators, the new processors deliver up to 42% higher inference performance and low latency for large language models (LLMs).
New Gaudi3 Details
Intel acquired Gaudi technology with the 2019 acquisition of Habana Labs. Gaudi accelerators are specialized hardware components that efficiently perform AI-related tasks, such as deep learning and large-scale generative AI models.
The next generation Gaudi accelerator, Gaudi3, aims to enhance AI workloads with improved performance over its predecessor, Gaudi2. The Gaudi3 will feature a dual-chiplet design, a substantial ASIC, and multiple HBM3 (or HBM3E) memory stacks, providing significant advancements in AI processing capabilities. Intel says the new part will be available in 2024.
Notable improvements include four times higher BF16 performance, double the networking speed, and 1.5 times higher bandwidth than Gaudi2.
Intel aims to leverage the rising demand for generative AI hardware to secure a larger share of the accelerator market in 2024. Their Gaudi lineup has already gained recognition for its competitive total cost of ownership (TCO) and reasonable pricing.
In 2025, Intel plans to consolidate GPU and Gaudi capabilities into a product called Falcon Shores, further expanding its AI processing offerings.
Analysis
Emerald Rapids is Intel’s second upgrade within the Xeon family in less than a year, providing customers with increased compute power and faster memory while maintaining power efficiency.
The key enhancements in the Emerald Rapids processors are striking. With support for up to 64 cores per CPU, a nearly threefold increase in the maximum last-level cache compared to the previous generation, eight channels of DDR5 per CPU, and improved inter-socket bandwidth, the new parts deliver an impressive 21% average performance gain for general compute tasks and a 36% boost in average performance per watt across various workloads.
A standout feature of the Emerald Rapids processors is its use of specialized accelerators for tasks such as compression, encryption, and data analytics. The ability to configure processors with varying numbers of accelerator ‘devices’ offers flexibility based on workload requirements.
Intel’s evolution of its Gaudi accelerators, with the coming Gaudi3 set to outperform its predecessor, Gaudi2. Intel’s strategic focus on generative AI hardware positions them well to capture a more significant share of the accelerator market in 2024. This is one to watch, as the market for AI accelerators is increasingly competitive, with AMD recently detailing its MI300X.
Emerald Rapids and the upcoming Gaudi3 accelerator demonstrate its commitment to delivering high-performance solutions for AI, data center, and server workloads. These advancements align with Intel’s strategy to address the growing demand for AI processing while maintaining a focus on performance, power efficiency, and security. Intel is delivering precisely what’s required in today’s hypercompetitive compute market.





